Effects of electrical muscle stimulation on cerebral blood flow
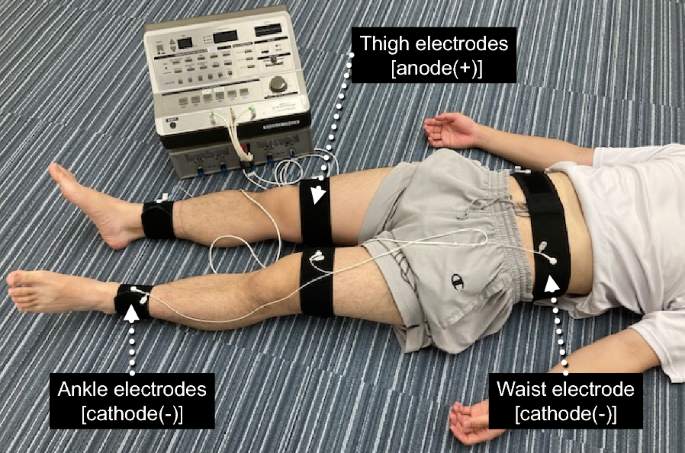
Effects of electrical muscle stimulation on cerebral blood flow
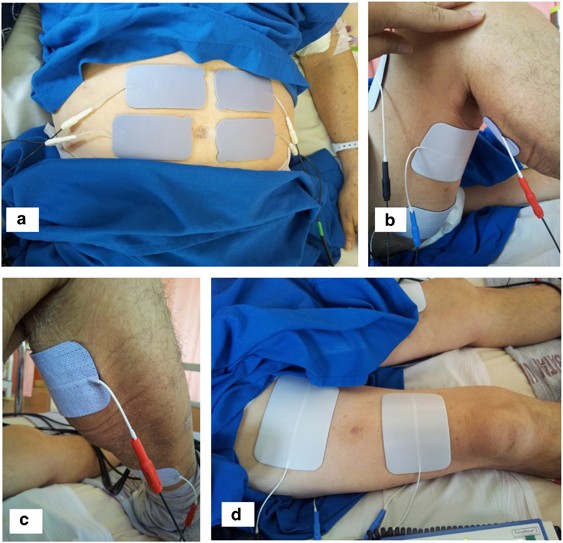
Electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) induces involuntary muscle contraction. Several studies have suggested that EMS has the potential to be an alternative method of voluntary exercise; however, its effects on cerebral blood flow (CBF) when applied to large lower limb muscles are poorly understood. Thus, the purpose of this study was to examine the effects of EMS on CBF, focusing on whether the effects differ between the internal carotid (ICA) and vertebral (VA) arteries. The participants performed the experiments under EMS and control (rest) conditions in a randomized crossover design. The ICA and VA blood flow were measured before and during EMS or control. Heart rate, blood pressure, minute ventilation, oxygen uptake, and end-tidal partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PETCO2) were monitored and measured as well. The ICA blood flow increased during EMS [Pre: 330 ± 69 mL min−1; EMS: 371 ± 81 mL min−1, P = 0.001, effect size (Cohen’s d) = 0.55]. In contrast, the VA blood flow did not change during EMS (Pre: 125 ± 47 mL min−1; EMS: 130 ± 45 mL min−1, P = 0.26, effect size = 0.12). In the EMS condition, there was a significant positive linear correlation between ΔPETCO2 and ΔICA blood flow (R = 0.74, P = 0.02). No relationships were observed between ΔPETCO2 and ΔVA blood flow (linear: R = − 0.17, P = 0.66; quadratic: R = 0.43, P = 0.55). The present results indicate that EMS increased ICA blood flow but not VA blood flow, suggesting that the effects of EMS on cerebral perfusion differ between anterior and posterior cerebral circulation, primarily due to the differences in cerebrovascular response to CO2.
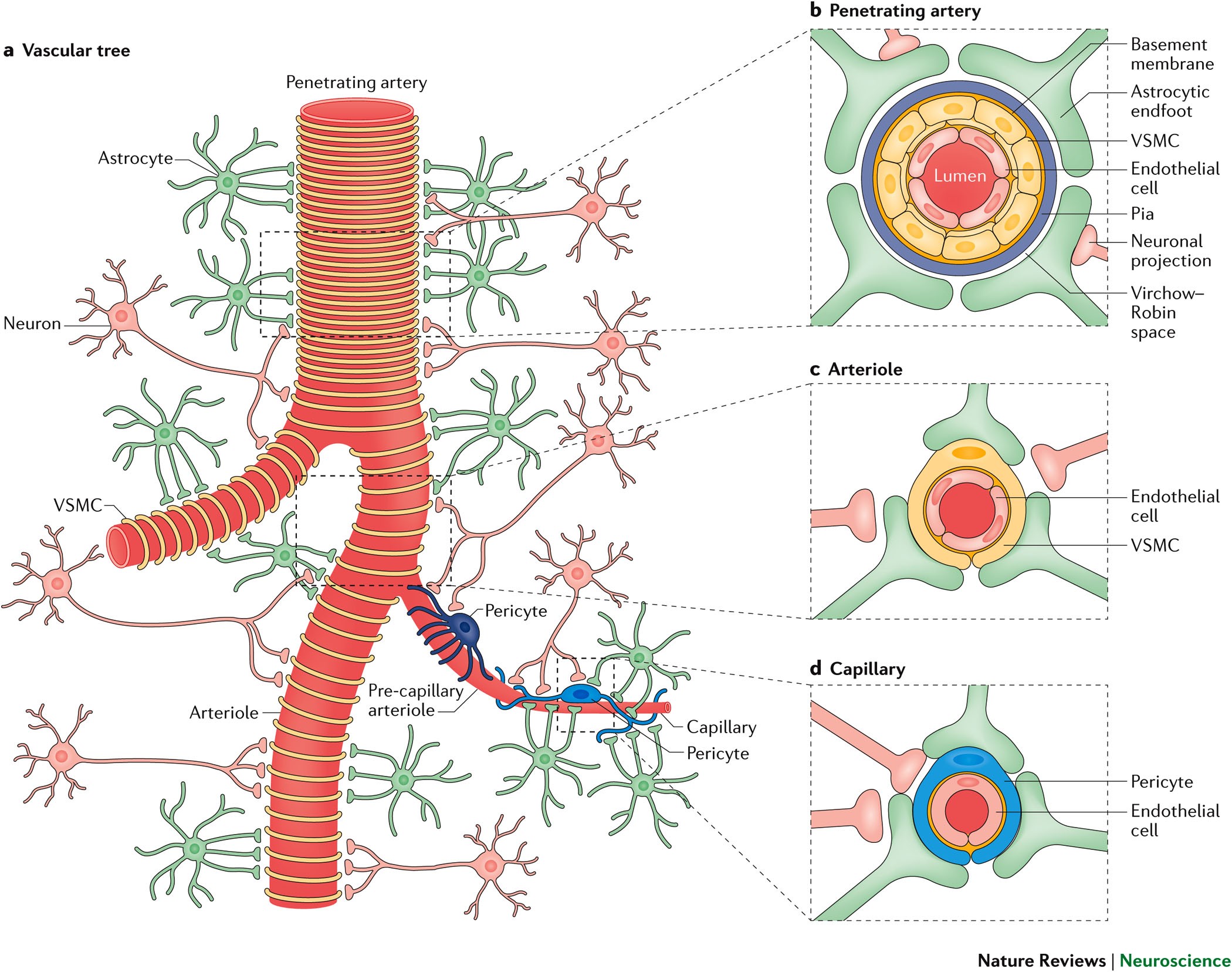
Cerebral blood flow regulation and neurovascular dysfunction in Alzheimer disease

Effects of tDCS dose and electrode montage on regional cerebral blood flow and motor behavior - ScienceDirect
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Personalised, image-guided, noninvasive brain stimulation in gliomas: Rationale, challenges and opportunities - eBioMedicine

The neuromodulatory role of dopamine in improved reaction time by acute cardiovascular exercise - Ando - The Journal of Physiology - Wiley Online Library
How Does Electrical Muscle Stimulation Work?

The Effect of a Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor on Neurovascular Regulation in Humans
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1290274850-a03f12de5a254e7c81854503fa91c205.jpg)
How Electrical Stimulation Is Used in Physical Therapy
Electrical stimulation-evoked contractions blunt orthostatic hypotension in sub-acute spinal cord-injured individuals: two clinical case studies

Regulation of cerebral blood flow in humans: physiology and clinical implications of autoregulation


